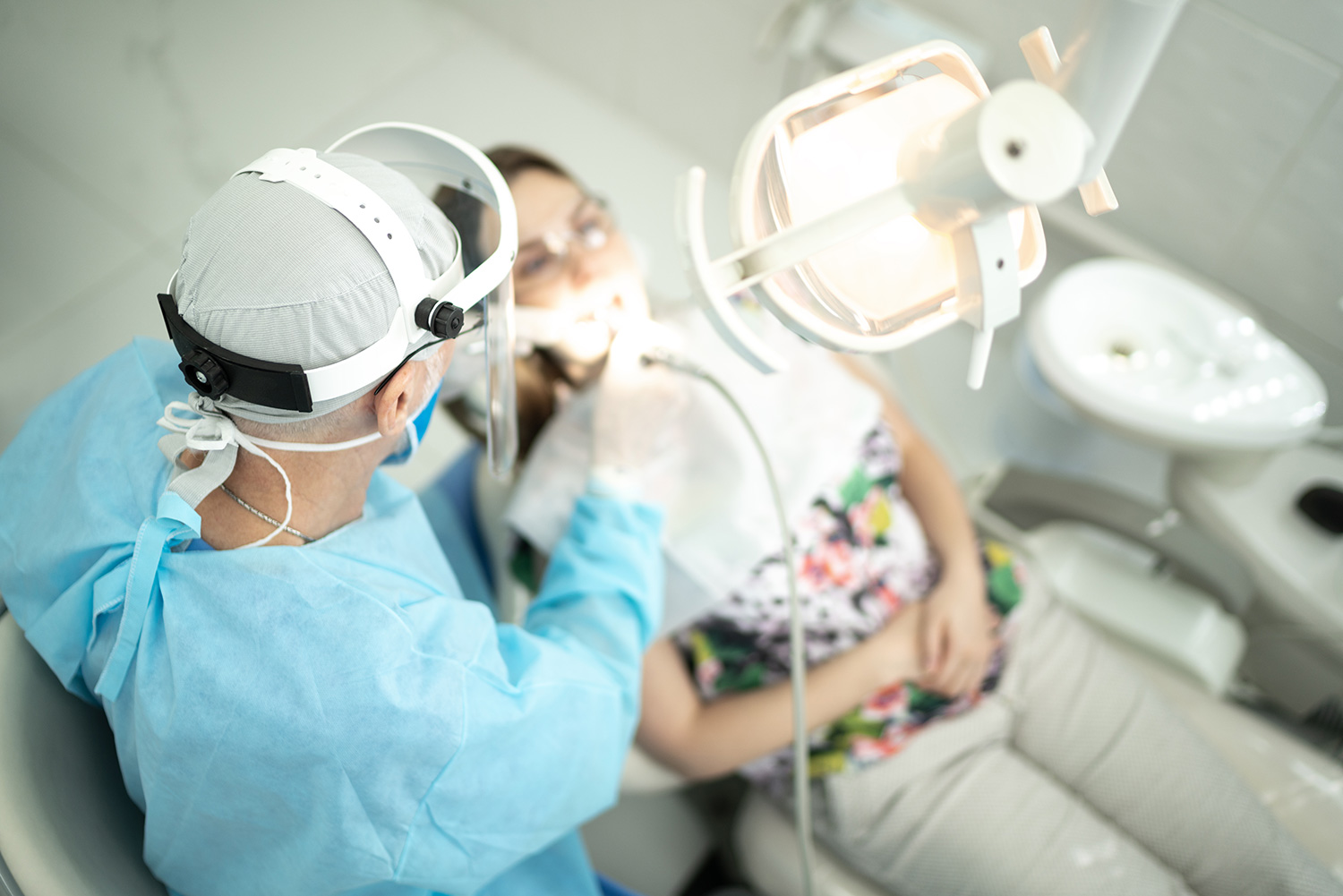
Reduce Healthcare Associated infections in 7 simple steps
Healthcare-Associated Infection (HAI) refers to infections that patients acquire during their healthcare treatment in various settings such as hospitals, clinics, or long-term care facilities. These infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms. Preventing HAIs is crucial to ensure patient safety and reduce the spread of infections. Healthcare facilities often have infection control departments or specialists who develop comprehensive infection prevention programs based on guidelines from reputable organisations such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organisation (WHO).
To prevent HAIs, several strategies can be employed:
- Hand hygiene: Proper hand hygiene is the most fundamental and effective measure to prevent infections. Healthcare providers should wash their hands with soap and water or use alcohol-based hand sanitisers before and after every patient contact.
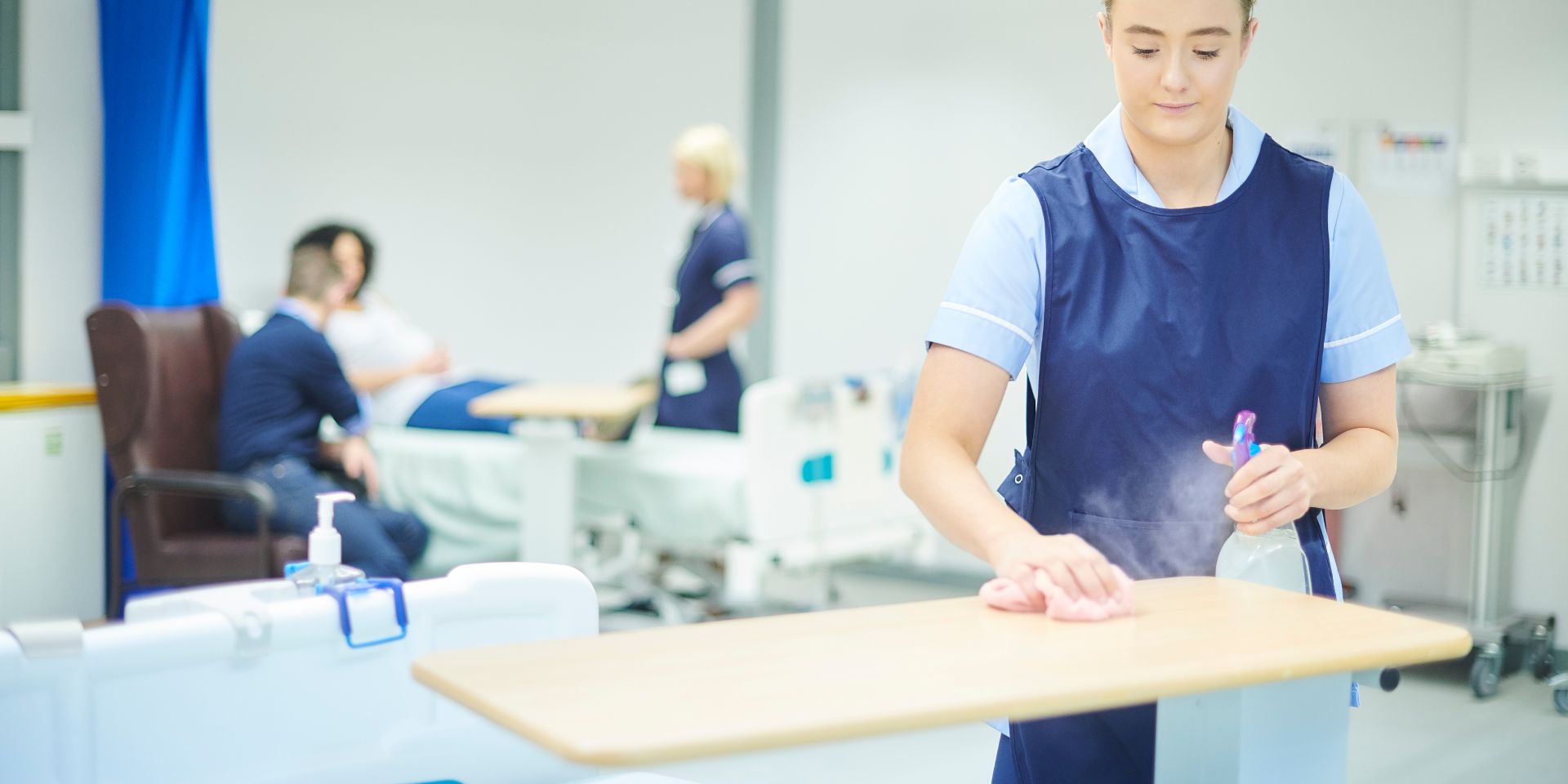
- Proper disinfection and sterilisation: Ensuring that medical equipment, instruments, and surfaces are properly cleaned, disinfected, or sterilised is essential to prevent the spread of infections. Healthcare facilities should follow recommended guidelines for cleaning and sterilisation procedures.
- Standard precautions: Healthcare providers should adhere to standard precautions, which include wearing personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, masks, gowns, and eye protection when appropriate. These precautions are designed to prevent the transmission of infections from both recognised and unrecognised sources.
- Environmental cleanliness: Regular cleaning and disinfection of patient care areas, surfaces, and equipment are crucial in reducing the risk of infections. Proper maintenance of ventilation systems and controlling the spread of airborne pathogens are also important.
- Antibiotic stewardship: Overuse or misuse of antibiotics can contribute to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which pose a significant threat in healthcare settings. Implementing antibiotic stewardship programs helps ensure appropriate use of antibiotics, reducing the risk of infections and the development of resistant organisms.
- Vaccinations: Immunisations play a vital role in preventing infections such as influenzas, hepatitis B, and pneumococcal disease.
- Education and training: Healthcare professionals should receive ongoing training on infection prevention protocols and stay updated on best practices. Patient education regarding infection prevention, hand hygiene, and other preventive measures can also be helpful.
By implementing strategies, healthcare facilities can work towards minimising HAIs, protecting patient safety, and improving overall healthcare quality.
More News

Are you a new customer, or have question about a product or project? We’re here to help.

We value connection with our customers, distributors, and the community. Reach out today with your questions and enquiries.